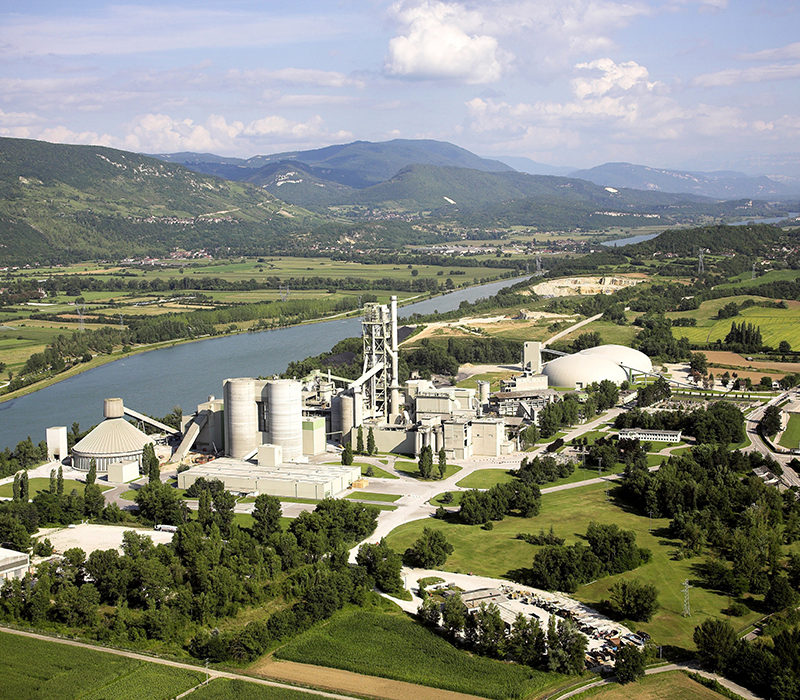
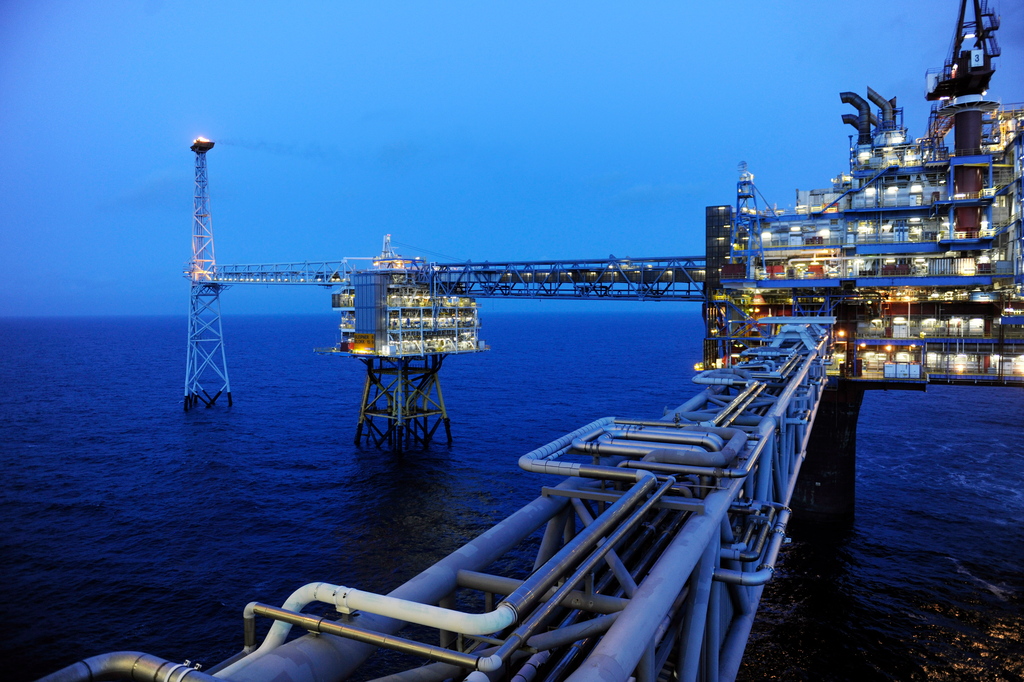
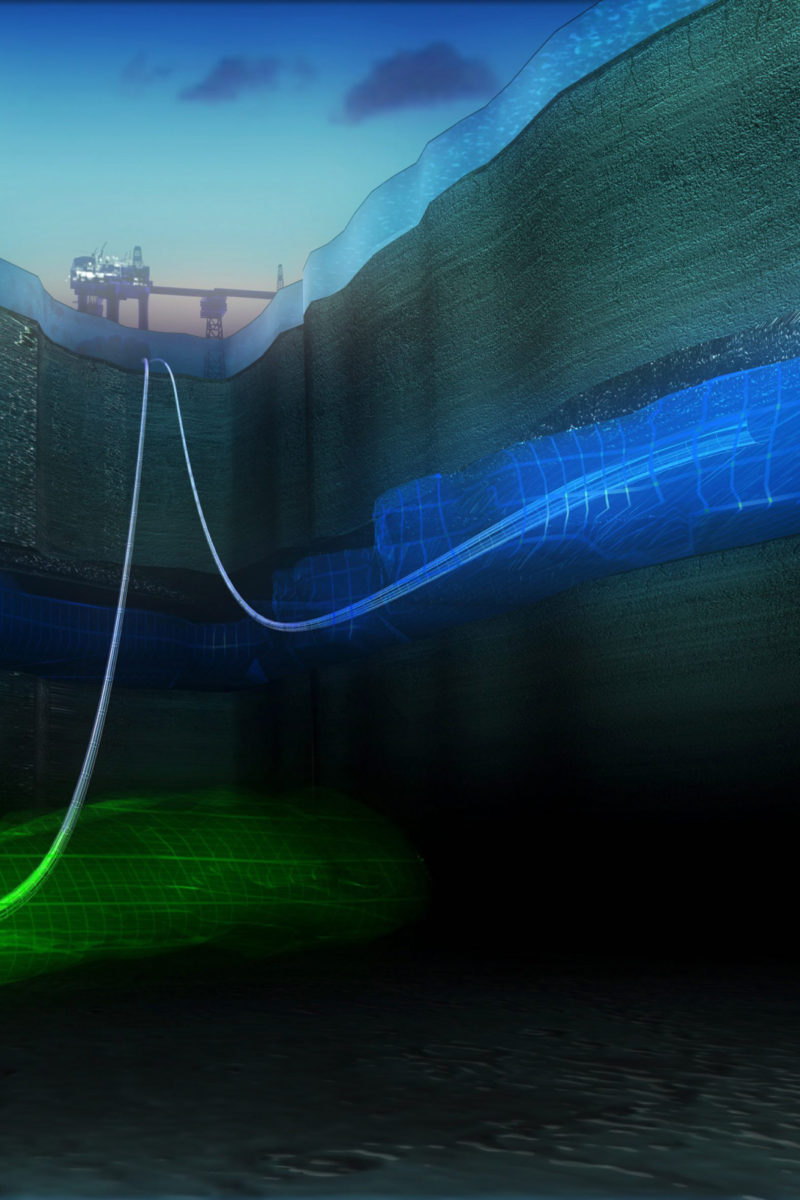
Multiple industries sharing CO2 transport and storage infrastructure, enabling these industries to achieve net zero emissions
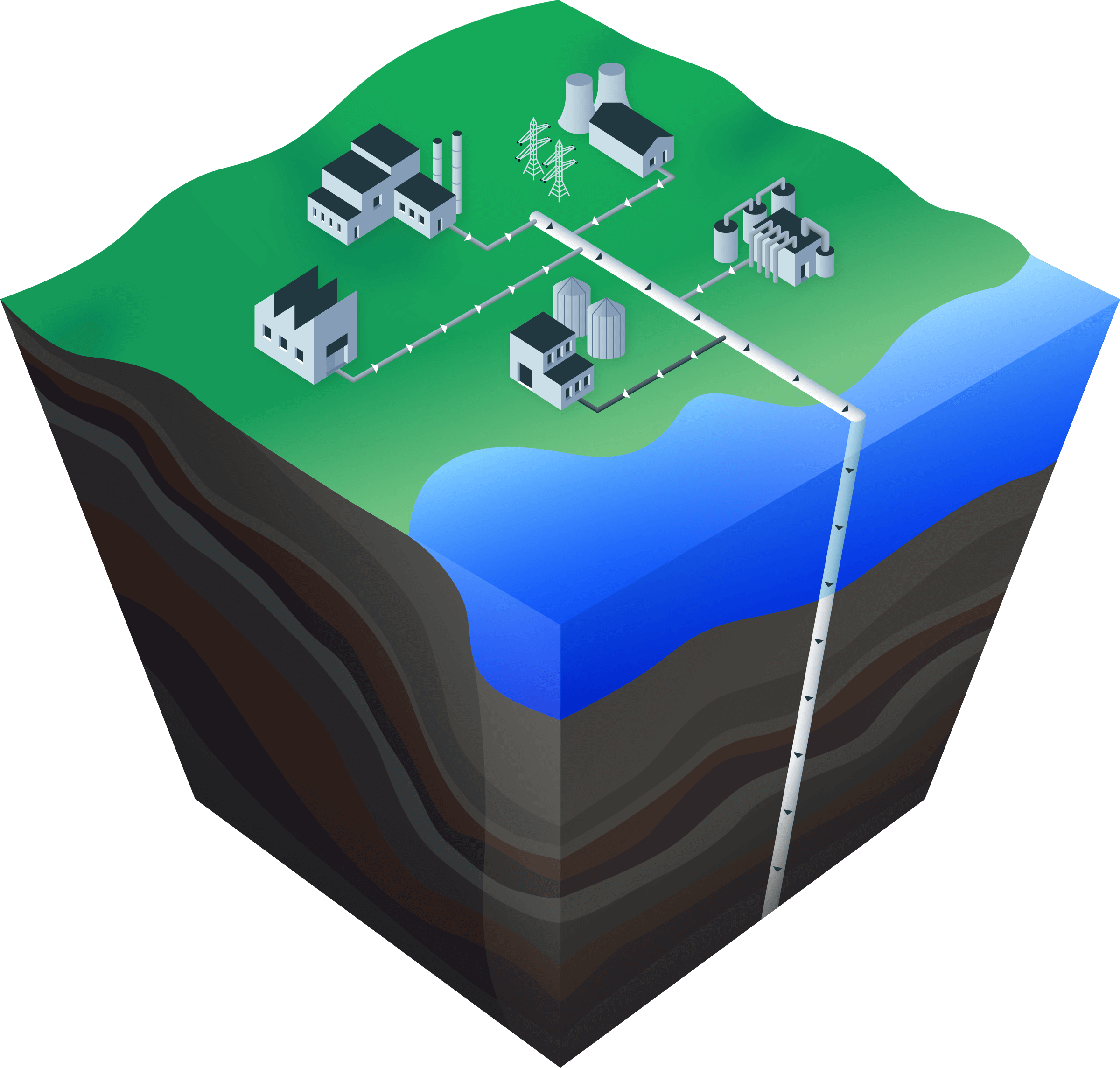
Gas Removal
CCUS underpins the removal of CO2 from the atmosphere through bioenergy with CCS (BECCS) and Direct Air Capture and Storage (DACS)
CCUS enables the production of clean industrial products such as clean steel and cement
CCUS provides a source of flexible, low-carbon power generation
CCUS represents one of the main routes for clean hydrogen production - a key solution for low-carbon heating in homes and industry, as well as clean transport
Captured CO2 can also be used to make products, such as synthetic fuels and low-carbon building materials, or in the food and beverage industry
CCUS underpins the removal of CO2 from the atmosphere through bioenergy with CCS (BECCS) and Direct Air Capture and Storage (DACS)
CCUS enables the production of clean industrial products such as clean steel and cement
CCUS provides a source of flexible, low-carbon power generation
CCUS represents one of the main routes for clean hydrogen production - a key solution for low-carbon heating in homes and industry, as well as clean transport
Captured CO2 can also be used to make products, such as synthetic fuels and low-carbon building materials, or in the food and beverage industry